Earth reached its closest point from the sun, January 4, at 1:36am EDT or January 4 at 6:36am in Universal Time (UT). This is called perihelion.
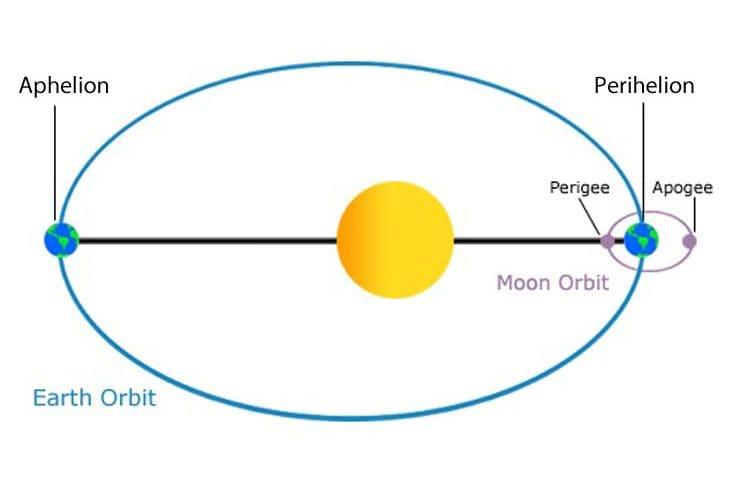
The point of closest approach is called perihelion. These terms are specific to a body orbiting the sun. For satellites of Earth (including the moon), the points of farthest and closest approach are called apogee and perigee, respectively. The generic terms for farthest and closest approach of a body in an elliptic orbit about a larger body are apoapsis and periapsis, respectively.
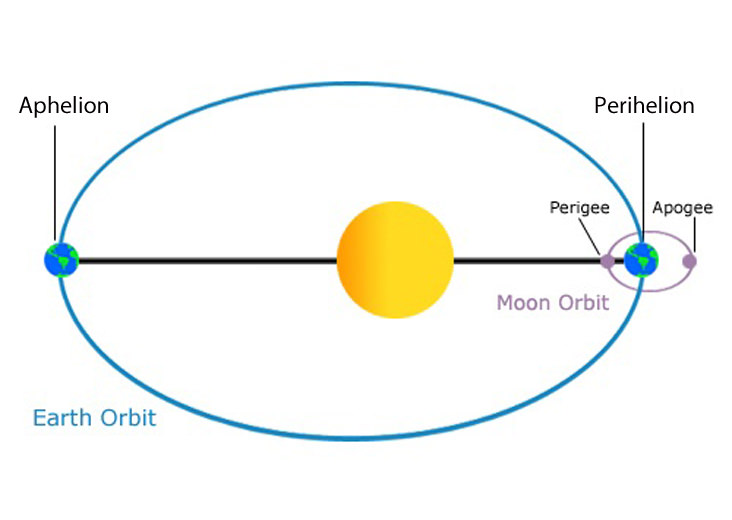
Aphelion versus perihelion. (orbits exaggerated). Image credit: NOAA/NASA.
The diagram below shows the times and positions of the Earth during the solstices, equinoxes, perihelion and aphelion as it orbits the sun over a year.

This diagram shows the relation between the line of solstice and the line of apsides of Earth’s elliptical orbit. The orbital ellipse (with eccentricity exaggerated for effect) goes through each of the six Earth images, which are sequentially the perihelion (periapsis—nearest point to the sun) on anywhere from 2 January to 5 January, the point of March equinox on 20 or 21 March, the point of June solstice on 20 or 21 June, the aphelion (apoapsis—farthest point from the sun) on anywhere from 4 July to 7 July, the September equinox on 22 or 23 September, and the December solstice on 21 or 22 December. credit: http://bit.ly/1pQn7wy
A common misconception is that seasons are caused by our distance from the sun. At aphelion Earth is 1.0167 Astronomical Units (AUs) or 152,096,000 kilometers from the sun and during perihelion it is 0.9833 AU or 147,098,290 kilometers from the sun. But the times of greatest solar radiation on a hemisphere happen not because of the distance between the Earth and sun but the tilt of Earth’s rotation axis. These times are during the December and June solstices.

Solar apparent size-perihelion versus aphelion 2012. The red circles show the size of one disk superimposed over the other. Shot by David Dickinson and discussed in http://bit.ly/1pQmrHG
David Dickinson observed the sun with his own telescope during perihelion and aphelion in 2012 to create the above images. They show the sun from Earth on January 4th (perihelion) and July 4th (aphelion.) You can read more about his observations as well as perihelion and aphelion in his July 2, 2013 post on Universe Today.




