EARTH
We Live in the Sun’s Atmosphere 🌍☀️
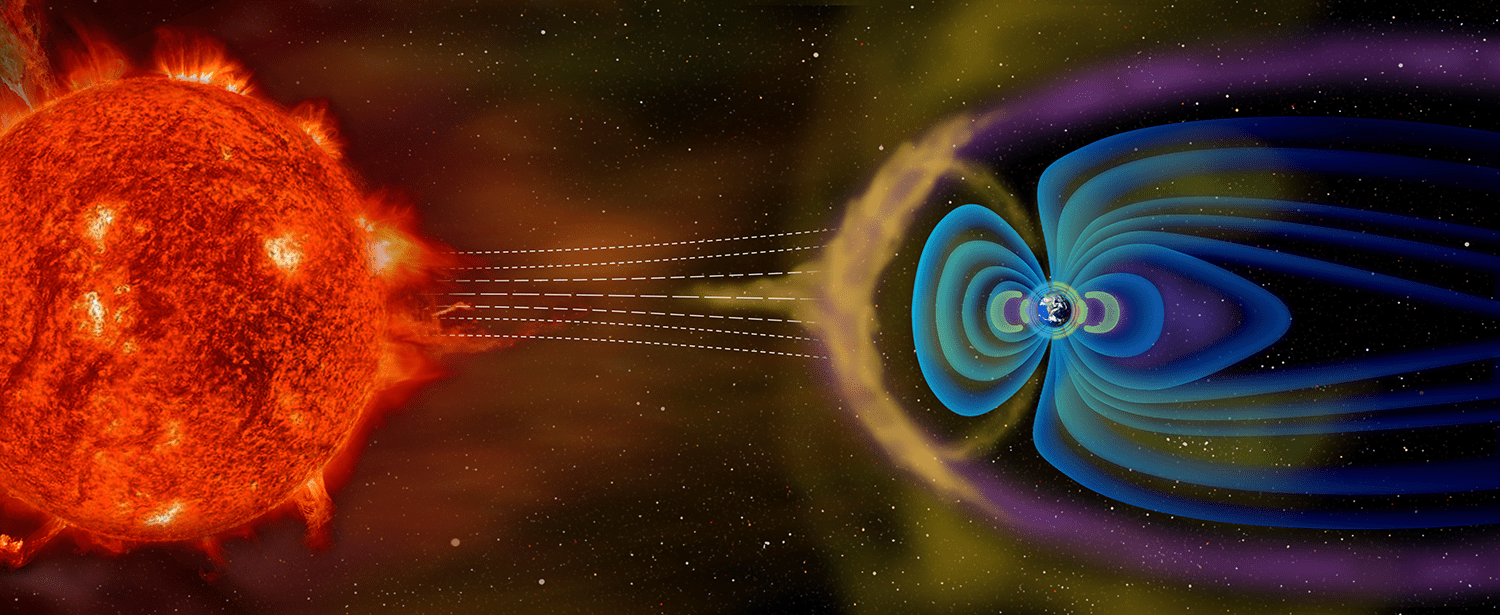
The Earth resides within the Sun’s vast, dynamic atmosphere, known as the heliosphere—a “bubble” of solar wind and magnetic fields that extends far beyond the planets and shapes the entire space environment.
The Earth’s own atmosphere is full of action when hit with space weather from the Sun, creating beautiful phenomena like auroras and impacting technology, communications, and power grids here on the ground. The planet’s magnetosphere shields it from solar radiation, and space weather, driven by the Sun, creates stunning auroras while also affecting our technology.
NASA and other space agencies have launched multiple missions in near-Earth orbit to study Earth’s relationship with the Sun, focusing on space weather, the magnetosphere, and how these interactions impact life on Earth.
Earth plays a key role in celestial phenomena, from eclipses and transits to the shifting seasons and orbits, with its position and movement contributing to significant events like the equinoxes and solstices, all of which influence life on Earth in profound ways.
Helio Missions: Near-Earth Orbit Explorations 🚀
NASA and other space agencies have launched numerous missions in near-Earth orbit (NEO) to better understand our planet’s relationship with the Sun. These missions explore a range of scientific questions, from the nature of space weather to monitoring the health of our magnetosphere. These orbiters and satellites are essential for understanding how Earth’s atmosphere interacts with the solar wind and how space weather can impact us here on the ground.
Find out more about heliophysics missions.
The Interactions Between Space Weather and Earth’s Atmosphere 🌌⚡
Aurora: The Sun’s Stunning Light Show 🌌✨
Space weather, primarily driven by the Sun, interacts with Earth’s atmosphere, creating stunning phenomena such as the aurora borealis (Northern Lights) and aurora australis (Southern Lights). These beautiful light displays occur when charged particles from the Sun collide with Earth’s magnetosphere and ionosphere, creating glowing patterns in the sky. 🌟
For more information about auroras, visit our Aurora page.
Impacts of Space Weather on Earth ⚠️
While auroras are the most visible impact of space weather, there are other, more serious effects. Space weather can interfere with satellite communications, GPS systems, and even power grids on Earth. Solar flares and coronal mass ejections (CMEs) can cause radio blackouts, disturb satellite orbits, and induce electrical surges in power infrastructure, leading to disruptions in daily life. 🌍
To learn more about how space weather impacts Earth, visit our Space Weather Impacts page.
The Magnetosphere and Its Role in Earth’s Space Environment
Earth’s magnetosphere acts as a protective shield, generated by the planet’s natural magnetic field. This bubble of magnetic fields surrounds our planet, deflecting harmful solar radiation and charged particles. However, the magnetosphere is not static—it changes shape and size in response to solar activity, such as solar flares or coronal mass ejections (CMEs). These fluctuations can interfere with communication signals and electrical grids.
Protecting Earth from Space Weather ⚡🛰️
NASA studies the magnetosphere to understand how it protects Earth from the Sun’s energetic particles. This research is crucial because it helps us predict space weather events that can affect everything from satellite communications to power systems here on Earth. Studying our magnetosphere also provides insights into the broader physics of space and the complex electromagnetic interactions at play in the universe.
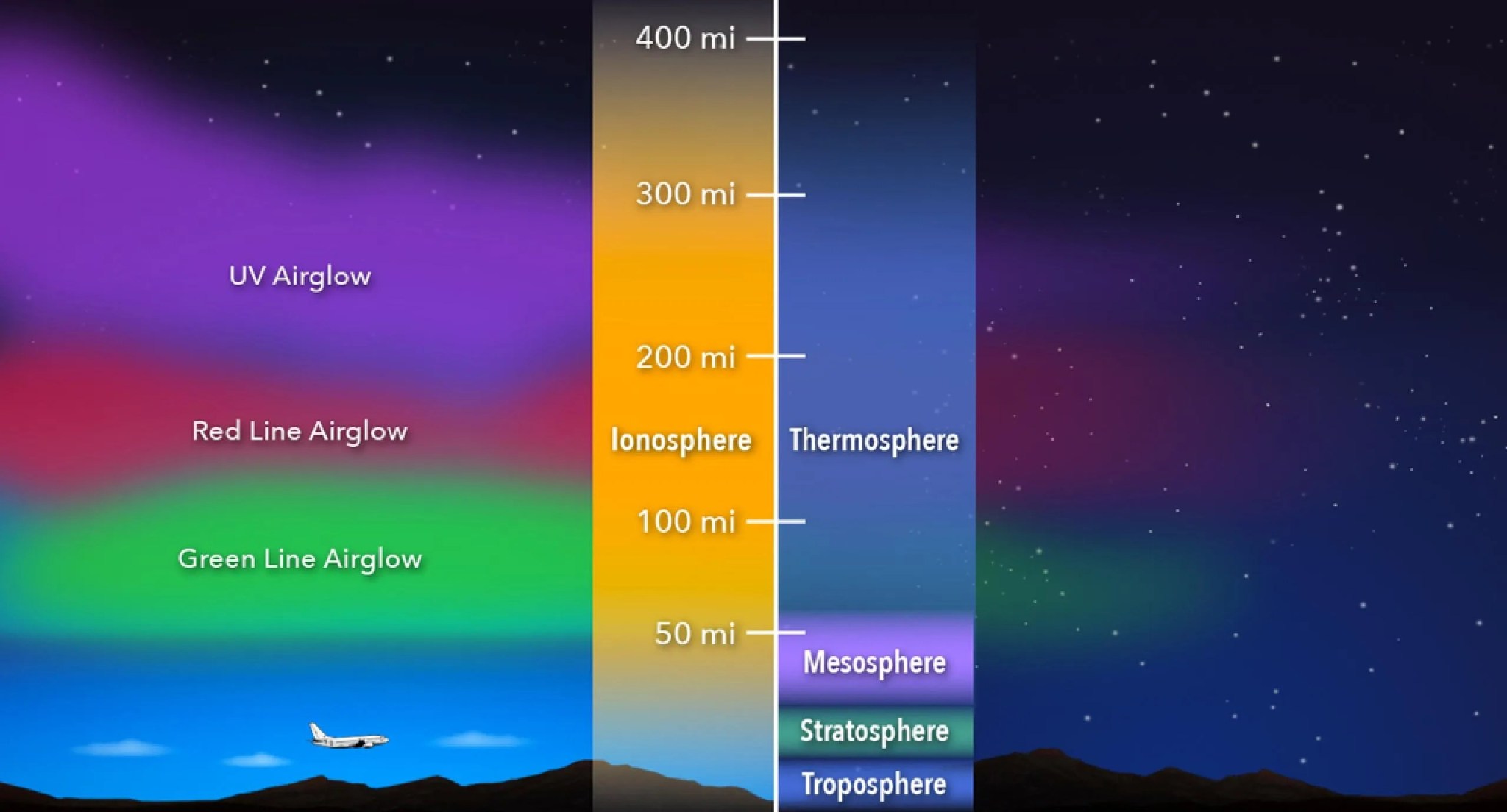
The Layers of Earth’s Atmosphere: Ionosphere, Thermosphere, and Mesosphere 🌌
NASA also focuses on studying the ionosphere, thermosphere, and mesosphere—the layers of Earth’s atmosphere where space weather phenomena, like auroras, occur. These layers are particularly sensitive to solar activity, and any sudden changes can have dramatic effects on human technology, especially on satellites and radio communications. The ionosphere, located about 50 to 300 miles above the Earth, is where electrically charged particles interact with solar radiation. When these interactions increase, it can lead to disruptions in radio signals and other communications.
The Sun and Earth’s Atmospheric Layers 🔥🌍
The thermosphere and mesosphere, which overlap with the ionosphere, play a crucial role in maintaining Earth’s space environment. These layers help protect us from harmful radiation while also contributing to the beautiful aurora displays seen at the poles. By studying the ionosphere-thermosphere-mesosphere system, scientists gain a better understanding of how space weather events unfold and how they impact life on Earth.
Earth’s Position and Movement in the Solar System 🌞🌍
The Earth’s movement through space and its position relative to the Sun and other planets plays a crucial role in phenomena like eclipses, seasons, and orbits. These events are not directly caused by the heliosphere, but they do shape the way we experience the Sun’s influence here on Earth.
Eclipses & Transits
Eclipses occur when the Earth, Sun, and Moon align in a way that blocks out the Sun’s light (solar eclipse) or the shadow of Earth falls on the Moon (lunar eclipse). Transits are when a planet, like Venus or Mercury, passes directly between Earth and the Sun, briefly appearing as a small dot moving across the Sun’s surface. These rare events give us valuable insights into the scale and movement of celestial bodies. 🌑☀️
For more information on eclipses, visit our Eclipse page, and to learn more about transits, check out our Transits page.

Equinoxes & Solstices
These are the moments when the Earth’s axis is tilted just right in relation to the Sun, creating equal day and night during the equinox, or marking the longest and shortest days of the year during the solstices. 🌞🌑
For more information on these events, read our blog posts on Orbits & Seasons.
Aphelion & Perihelion
The Earth’s orbit around the Sun is elliptical, which means at certain times of the year, we are closest to the Sun (perihelion) and farthest from it (aphelion). These variations slightly influence the seasons. 📅🌍
For more information on these events, read our blog posts on Orbits & Seasons.
IMAGE CREDITS: NASA

