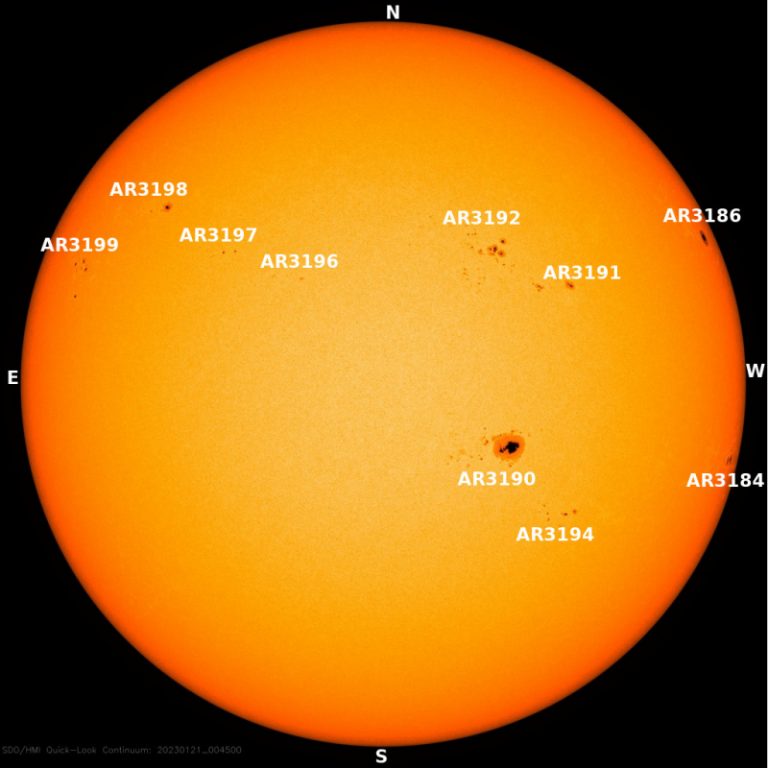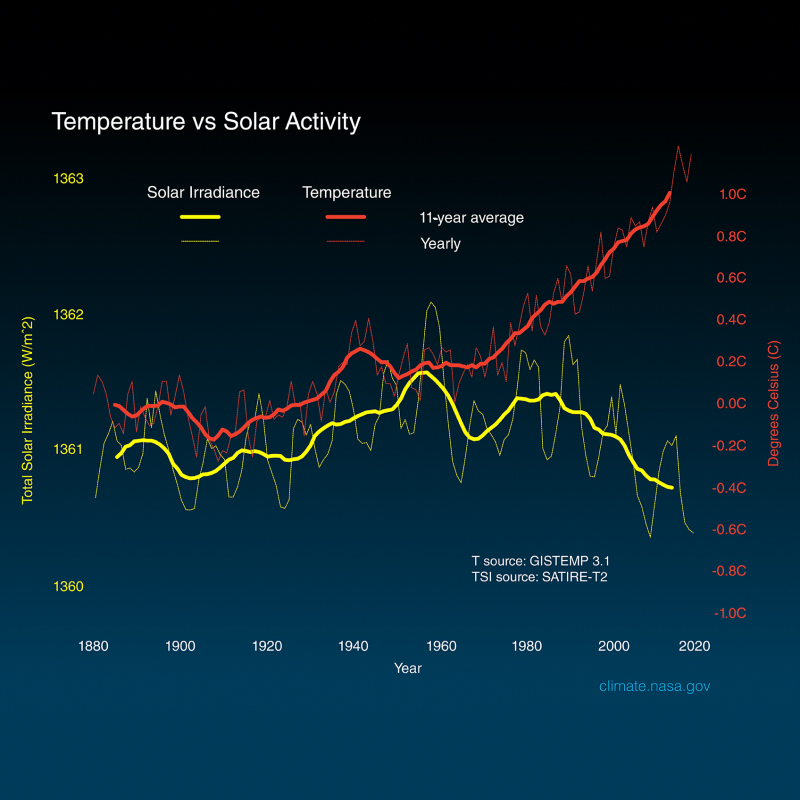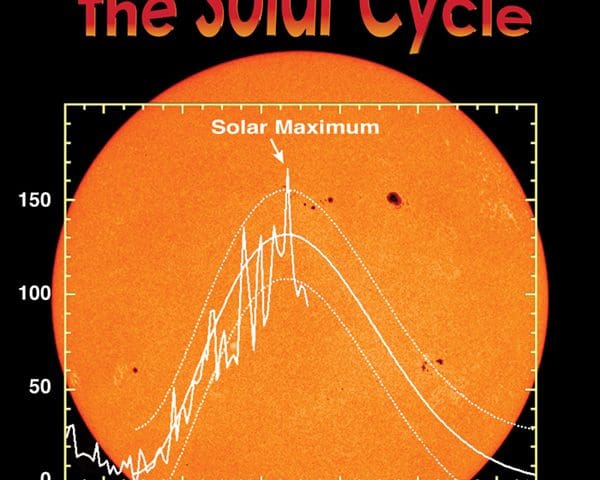
The Sun is not just a big bright ball. It has a complicated and changing magnetic field, which forms things like sunspots and active regions. The magnetic field sometimes changes explosively, spitting out clouds of plasma and energetic particles into space and sometimes even towards Earth. The solar magnetic field changes on an 11 year cycle. Every solar cycle, the number of sunspots, flares, and solar storms increases to a peak, which is known as the solar maximum. Then, after a few years of high activity, the Sun will ramp down to a few years of low activity, known as the solar minimum. This pattern is called the “sunspot cycle”, the “solar cycle”, or the “activity cycle”.
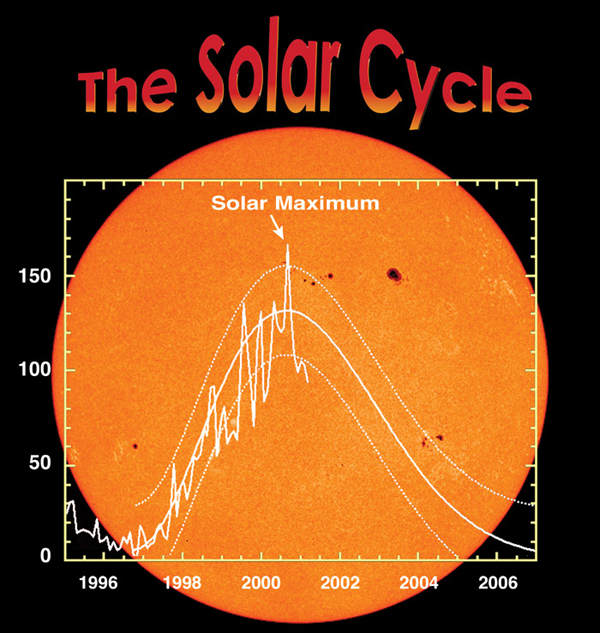
(credit: SOHO (ESA & NASA))